Relations in the Indo-Pacific
42 questions match this theme. View the archive for more.
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
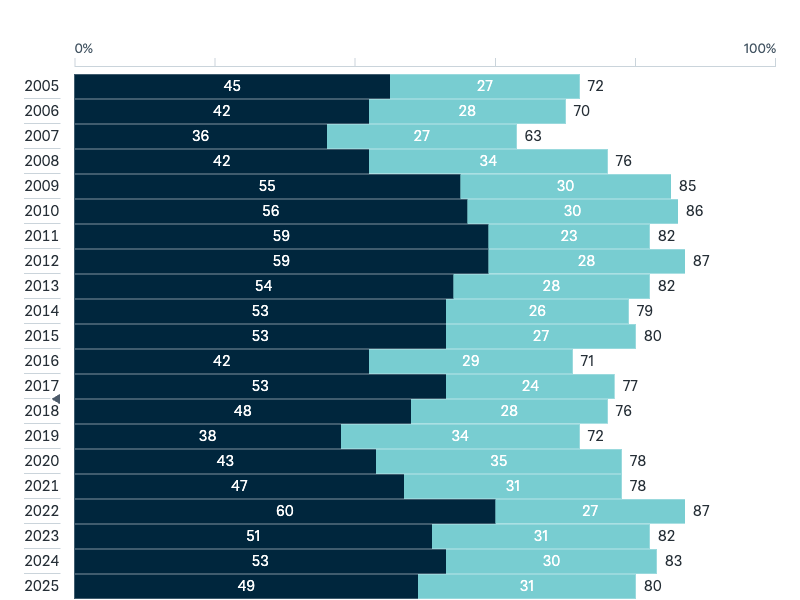
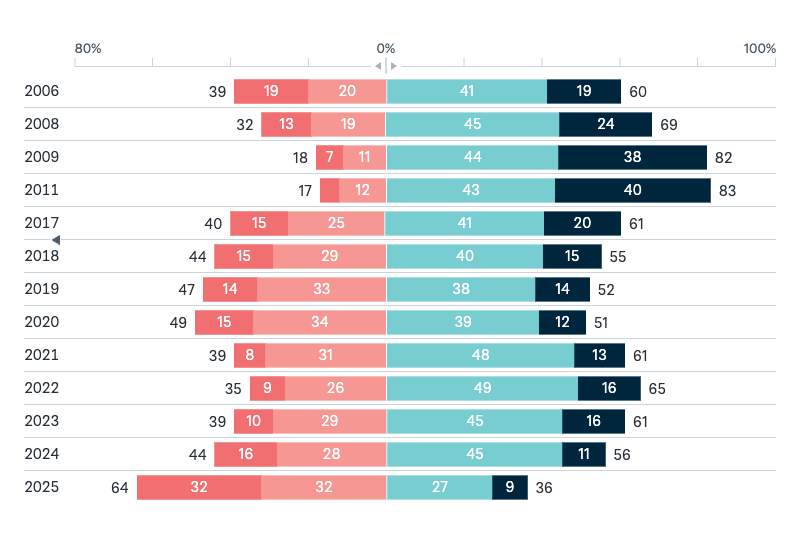
United States’ defence of Australia
Do you think the United States would or would not come to Australia’s defence if Australia were attacked by the military of another country?
Asked in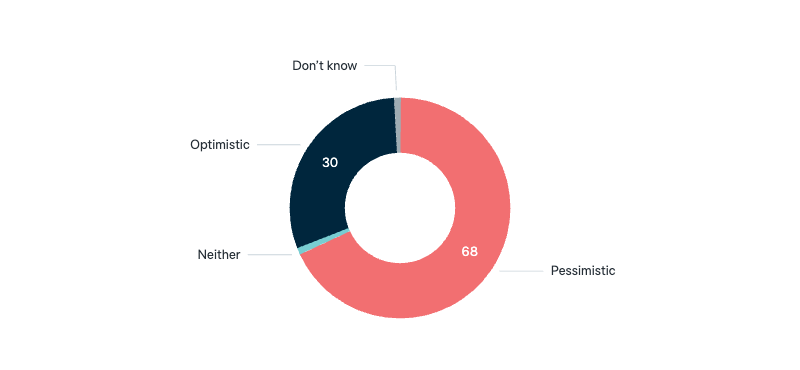
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
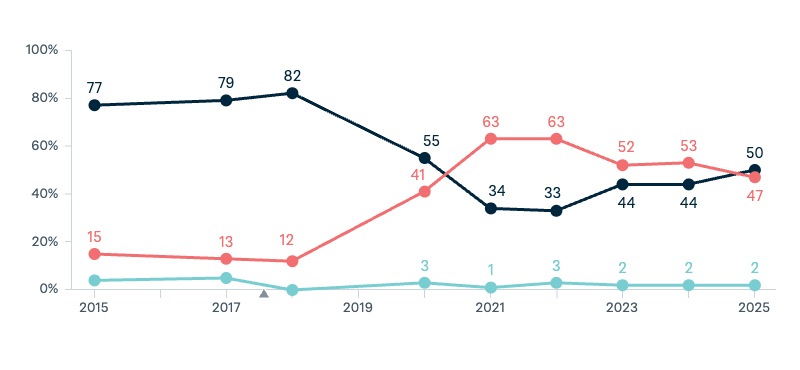
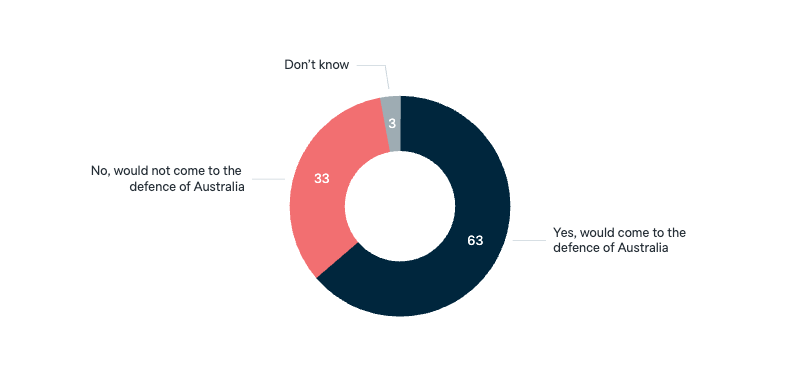
Donald Trump: optimism
Now thinking about the presidency of Donald Trump. Are you generally optimistic or pessimistic about the next four years with Donald Trump as US president?
Asked in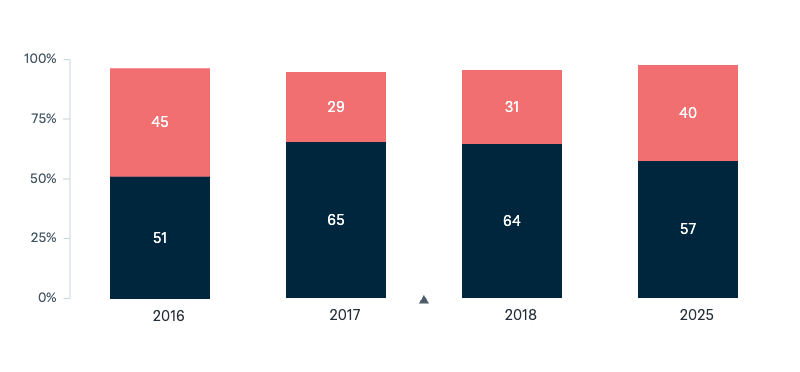
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
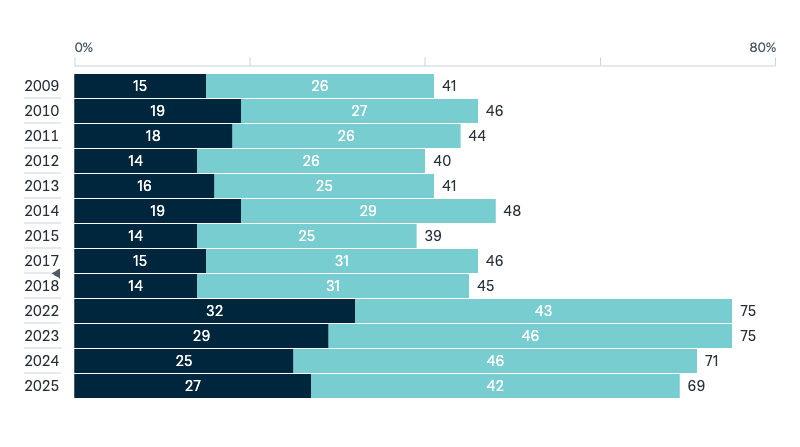
Australia and the United States under President Trump
Should Australia remain close to the United States under the presidency of Donald Trump?
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
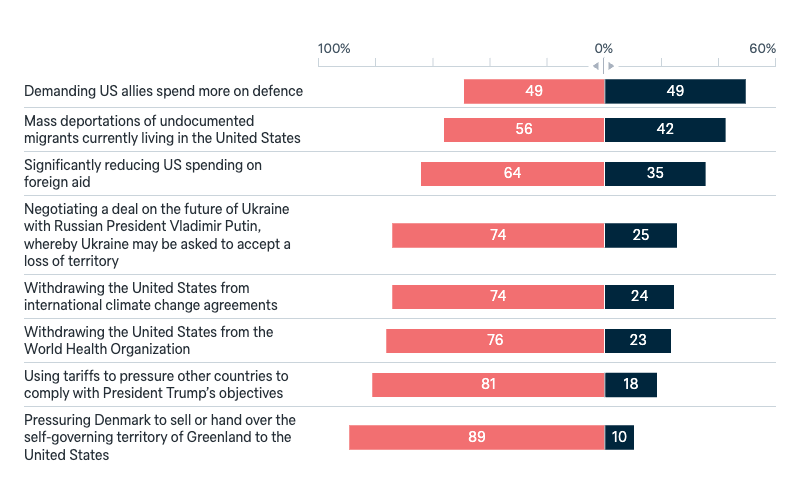
Policies of President Trump
Here are some policies of US President Donald Trump. Please indicate whether you approve or disapprove of each one:
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
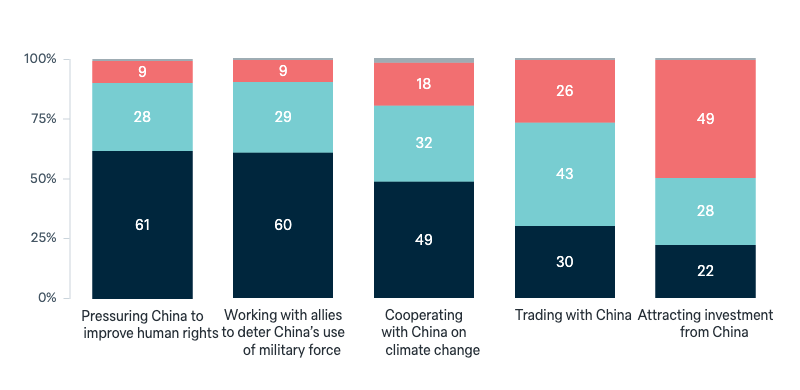
China: Australian policy settings
For each of the following, please indicate whether you think Australia should be doing more, less, or about the same as now:
Asked in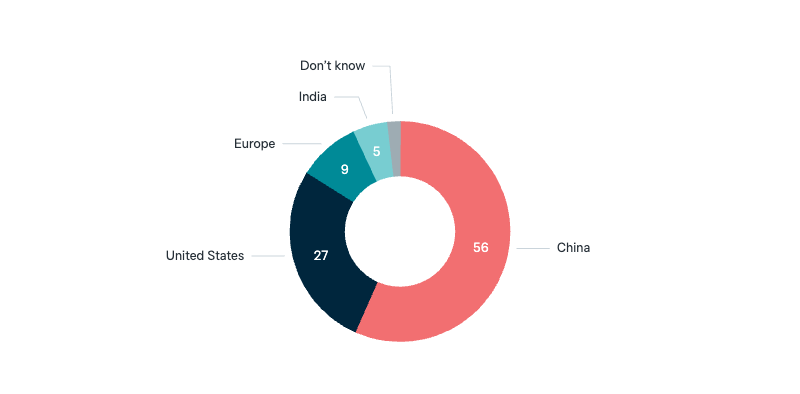
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
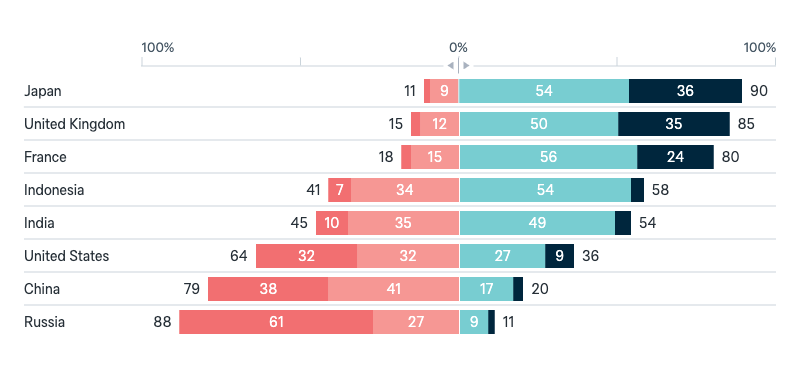
Superpowers in the future
Now a question about the role and influence of countries in the future. Ten years from now, which of these countries or regions do you think will be the most important and powerful in the world?
Asked in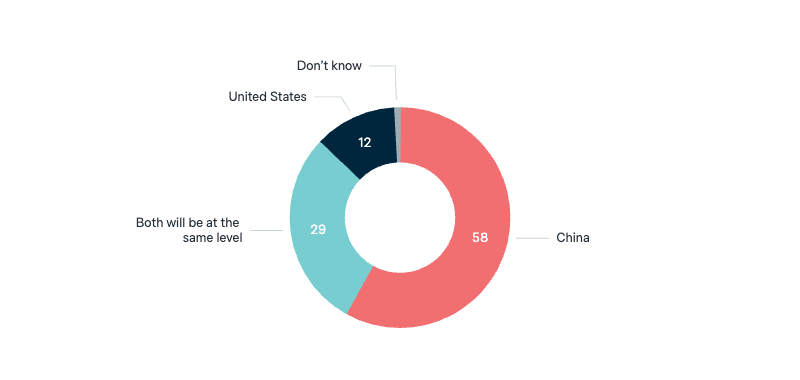
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
US–China technological competition
Next, thinking about technological innovation. Ten years from now, which of these countries do you think will be more advanced at developing and using the world’s most important technologies?
Asked in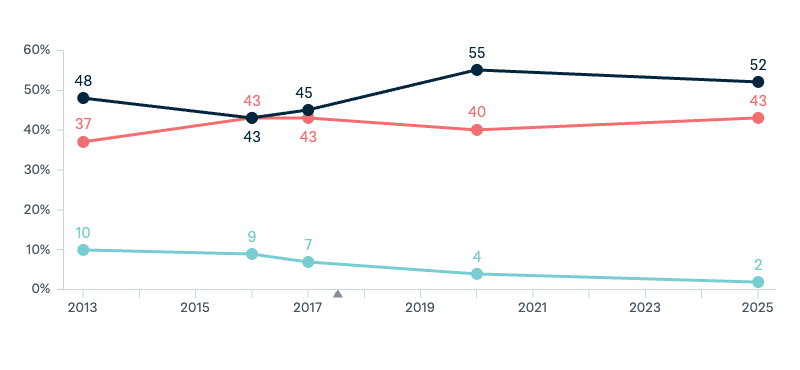
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
Relations with superpowers: United States and China
Is Australia’s relationship with China or the United States more important to Australia?
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
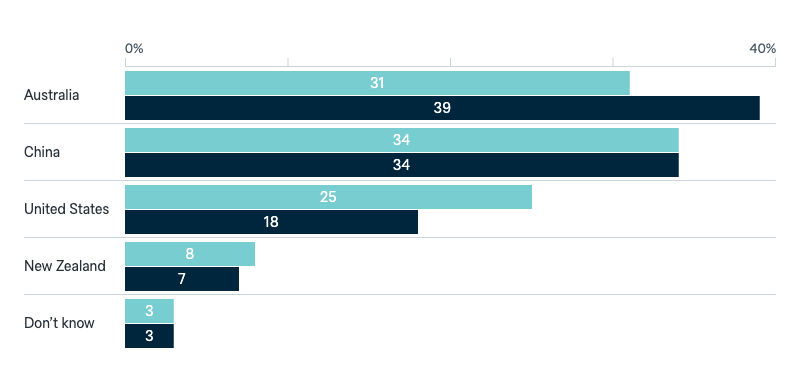
Influence in Pacific Island countries
Now thinking about the Pacific Islands region. In your opinion, which one of these countries has the most influence in Pacific Island countries?
Safety and threats
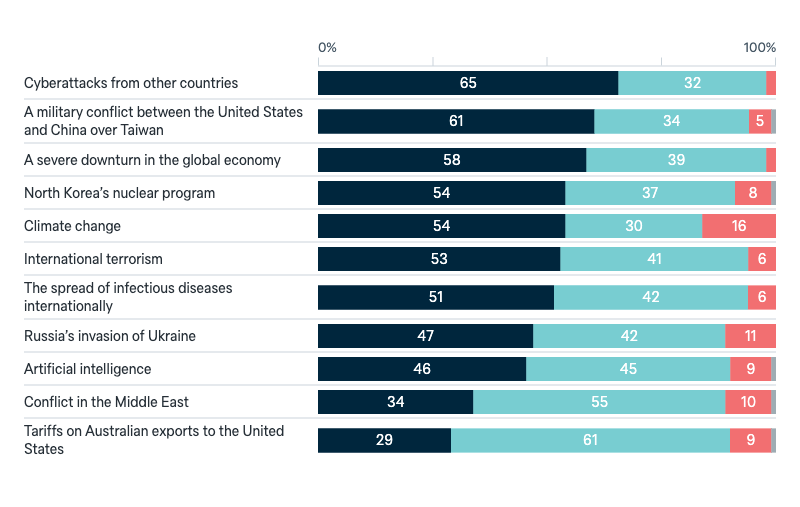
Threats to Australia’s vital interests
Do you see the following possible threat as a critical threat, an important but not critical threat, or not an important threat to Australia’s vital interests in the next ten years?
Questions from previous years
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
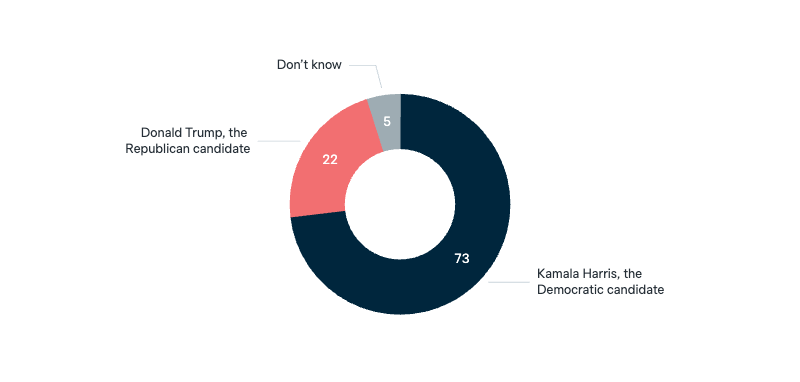
2024 US presidential election: Harris vs Trump
The US presidential election will be held in November this year. Which candidate would you prefer to see become president of the United States?
Asked in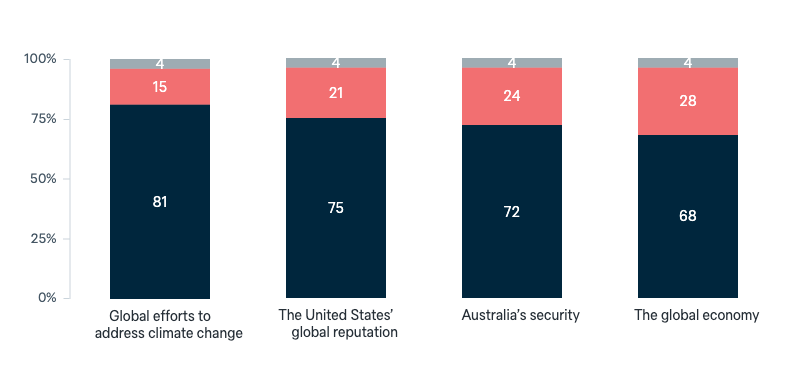
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
Harris vs Trump: by issue
Of the two US presidential candidates, which one do you personally think would be better for:
Asked in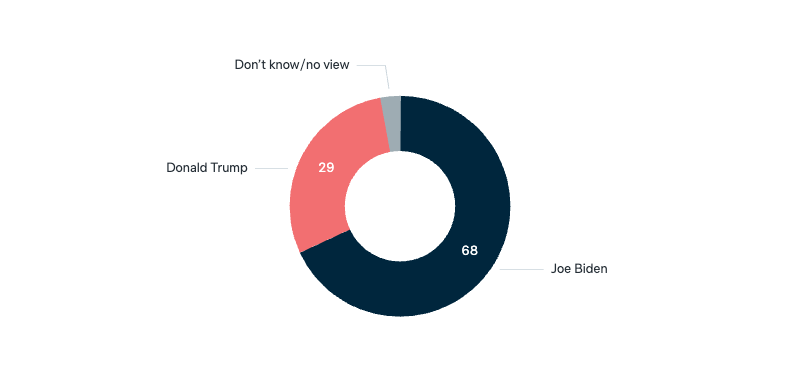
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
2024 US presidential election
Thinking about the upcoming 2024 US presidential election. If it came to a choice between Joe Biden and Donald Trump, who would you prefer to see elected as the US president?
Asked in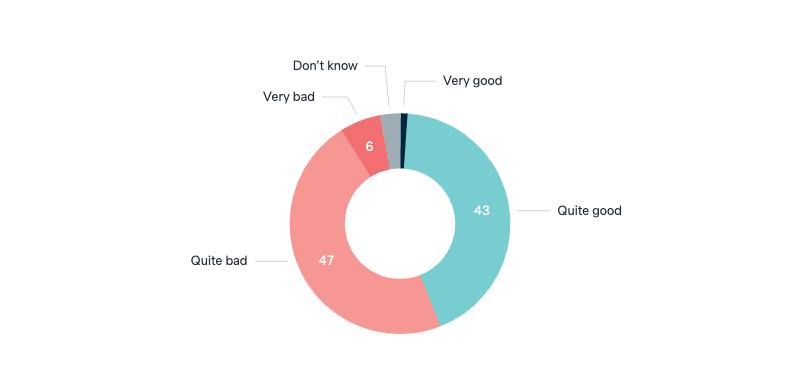
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
Australia–China relations
Now thinking about Australia’s relationship with China. On balance, how would you describe Australia’s current relationship with China?
Asked in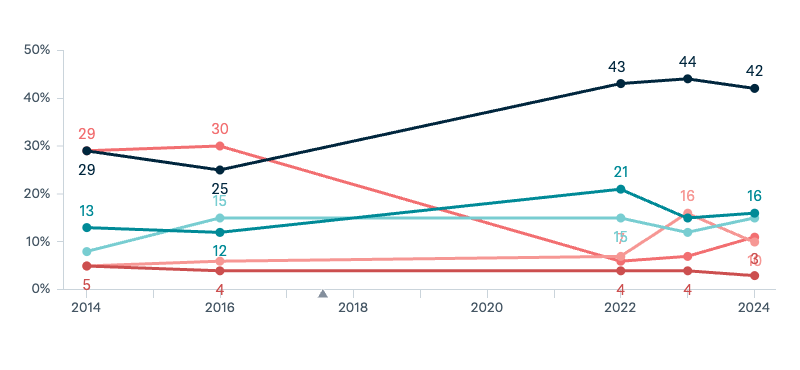
Global powers and world leaders
Australia’s best friend in Asia
Which one of the following countries is Australia’s best friend in Asia?
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
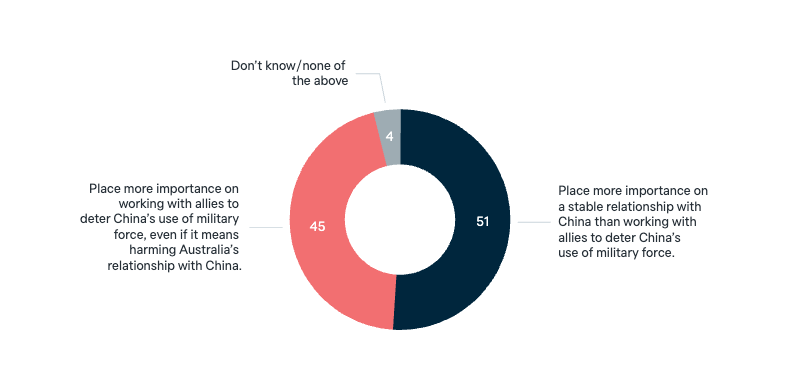
China: emphasis on deterrence or stability
Now thinking about how Australia should manage its relationship with China. Which one of the following statements comes closest to your view? Australia should…
Asked in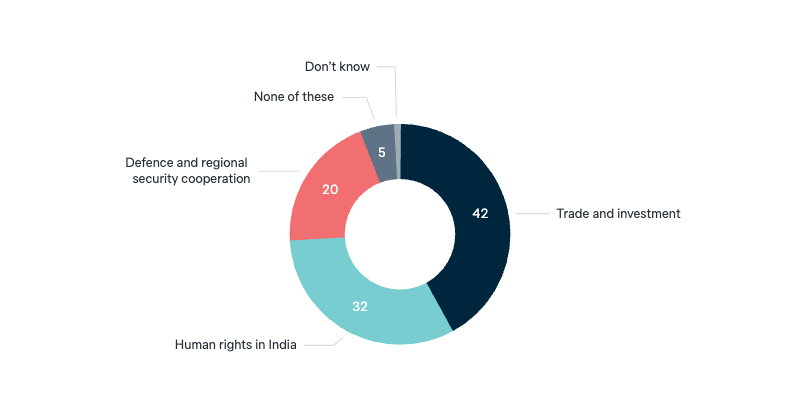
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
Highest priority for Australia’s relationship with India
Of these, which would you say Australia should give highest priority to in its relationship with India?
Asked in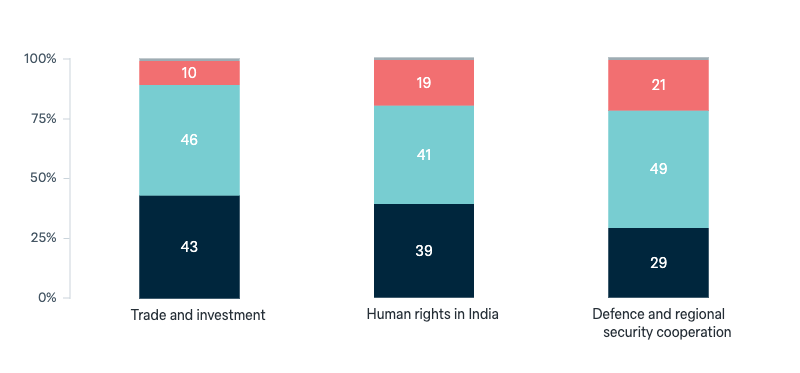
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
India: Australia’s relationship priorities
Now a question about India. In your view, what priority should Australia give to the following issues in its relationship with India:
Asked in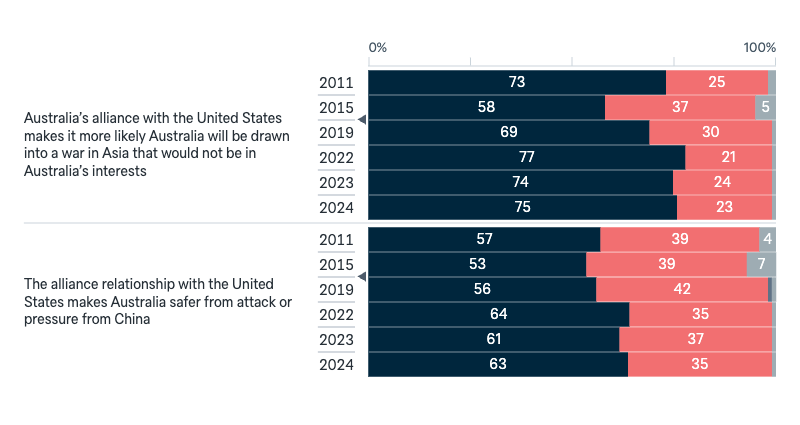
United States
US alliance: effect
I am now going to read you some different arguments about the alliance relationship with the United States. Please indicate whether you agree or disagree.
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
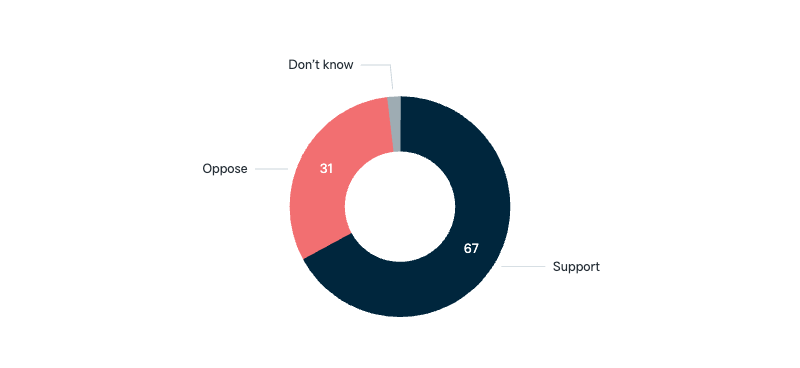
Visa requirements for citizens of Pacific Islands countries
Would you support or oppose relaxing visa requirements for citizens of Pacific Islands countries to enable them to live, work and study in Australia?
Asked in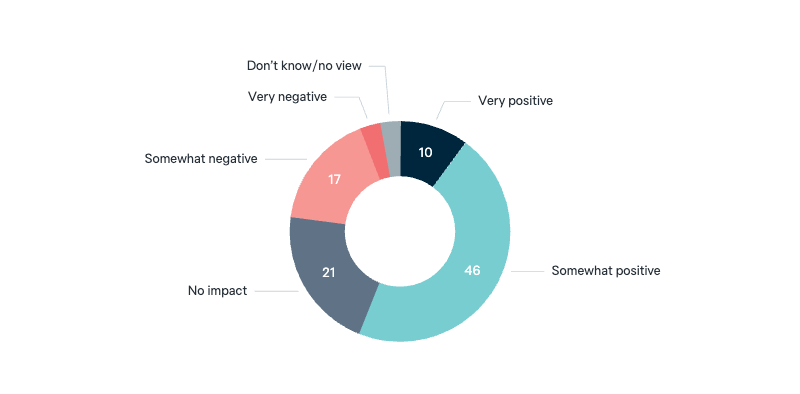
China
Australia–China ministerial contact
Over the last twelve months, there has been a resumption of high-level ministerial contacts between the Australian and Chinese governments. In your opinion, what impact will this have on Australia’s national interests?
Asked in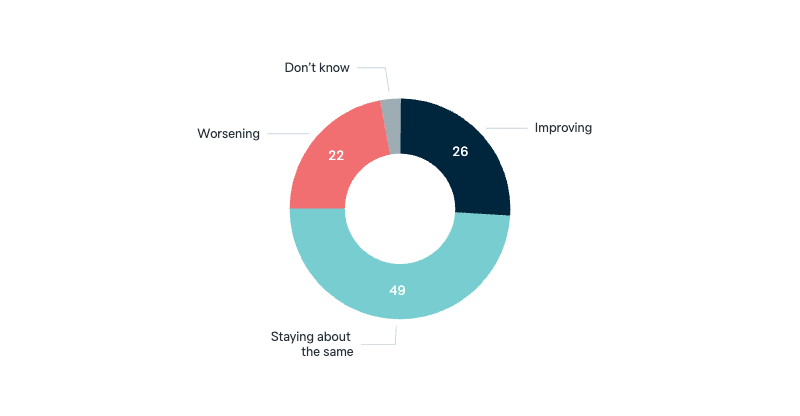
Australia and the Pacific
Australian relations with Pacific Islands countries
Now a question about the Pacific Islands. In your opinion are Australia’s relations with Pacific Islands countries improving, worsening or staying about the same?
Asked in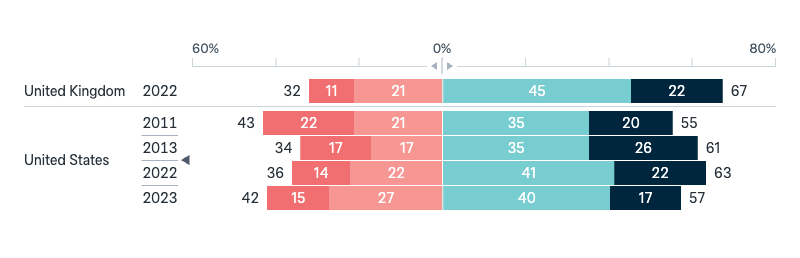
Defence and security
Foreign military based in Australia
Are you personally in favour or against Australia allowing the United States to base military forces here in Australia?
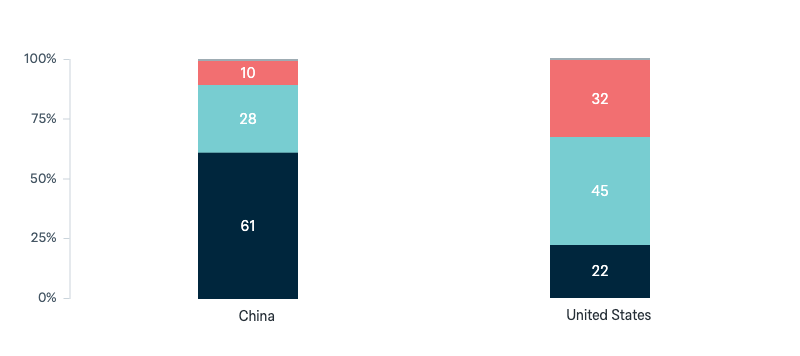
China
Future roles of the United States and China
Now a question about the role and influence of countries as world leaders in the future. Ten years from now, do you think the United States/China will play:
Asked in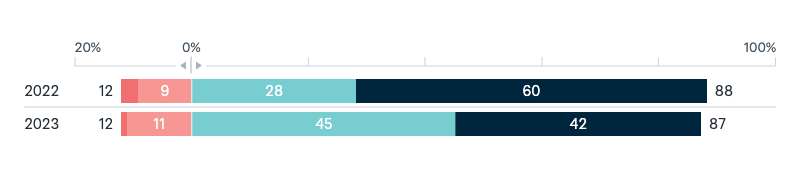
China
Potential Chinese military base in the Pacific
To what extent are you concerned or not concerned about China potentially opening a military base in a Pacific Islands country?
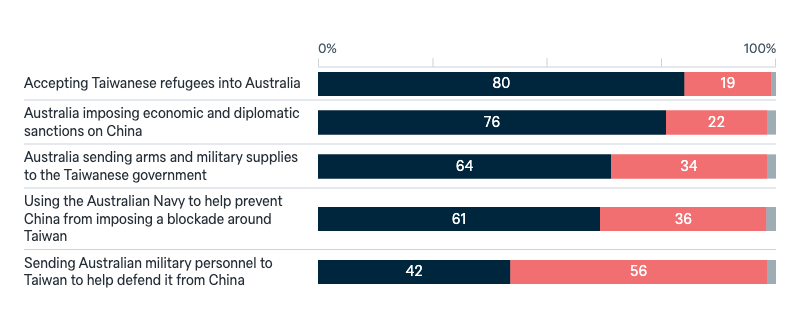
China
Potential conflict over Taiwan
If China were to invade Taiwan, would you support or oppose Australia, acting together with the United States, taking the following actions.
Asked in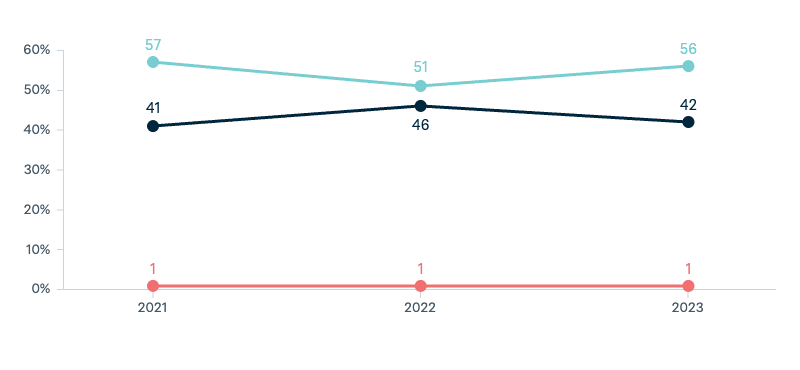
Defence and security
Potential military conflict between China and the United States
In the event of a military conflict between China and United States, please say which one of the following statements comes closest to your own personal view.
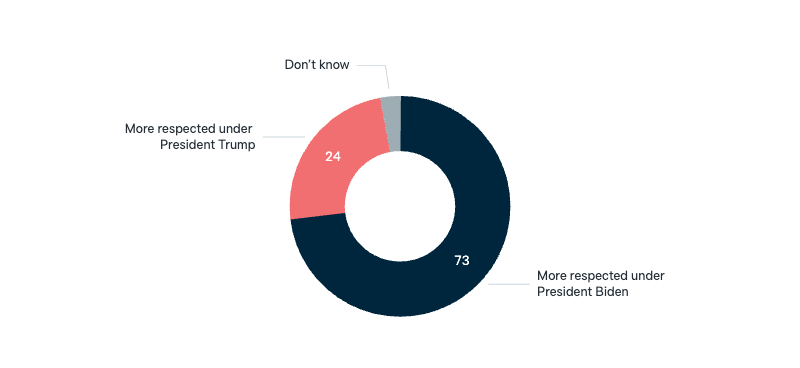
United States
Respect for the United States
In your opinion is the United States more respected in the world under President Joe Biden, or was it more respected under former President Donald Trump?
Asked in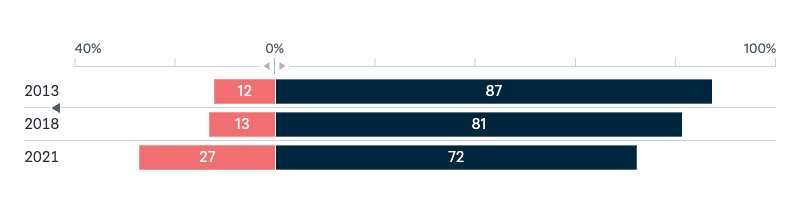
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
Good relations with the US and China
Is it possible to have good relations with both the United States and China?
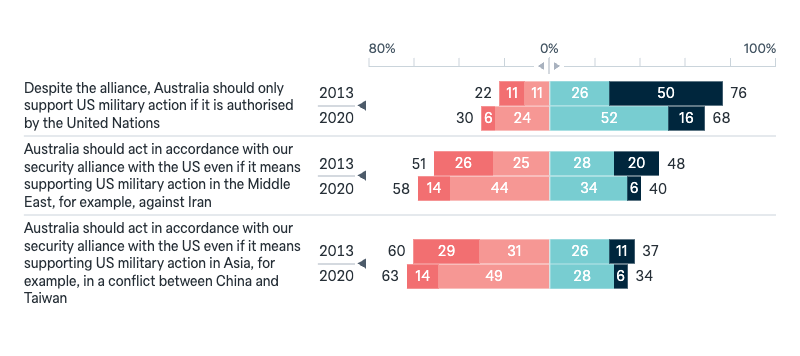
United States
Military action under ANZUS
Under what circumstances should Australia act in accordance with our military alliance with the United States?
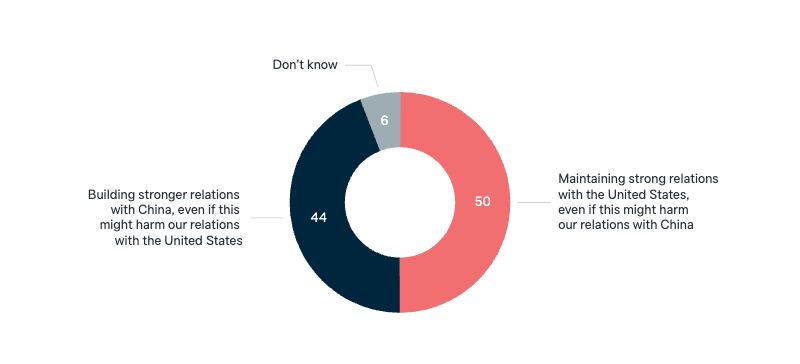
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
Relations with superpowers
Should the Australian government prioritise the United States or China, even if it may harm relations with the other?
Asked in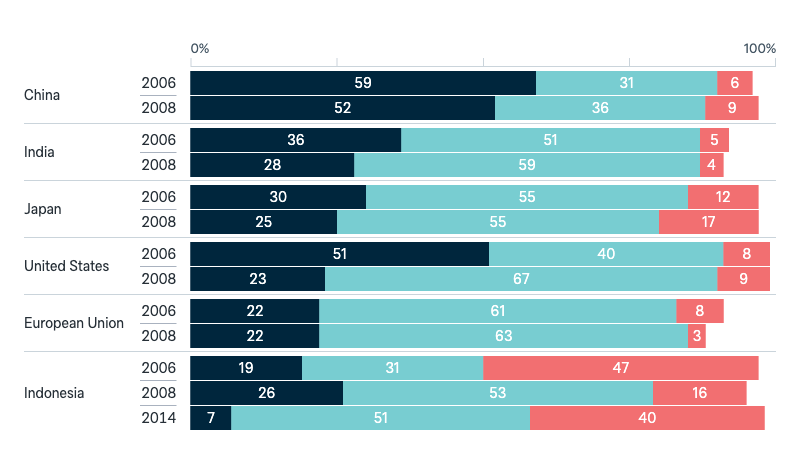
Australian foreign policy
Australia’s bilateral relationships
In your opinion, are Australia’s with the following countries improving, worsening, or staying about the same.
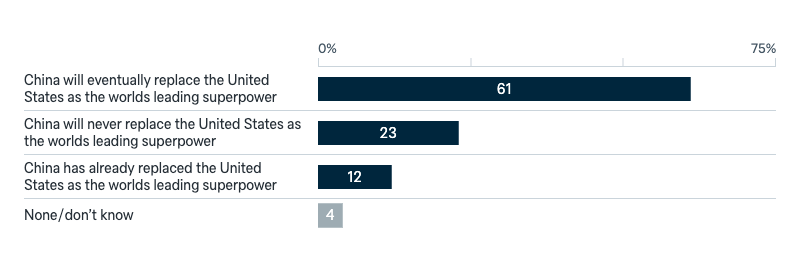
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
The world’s leading superpower
Will China replace the United States as the world’s leading superpower?
Asked in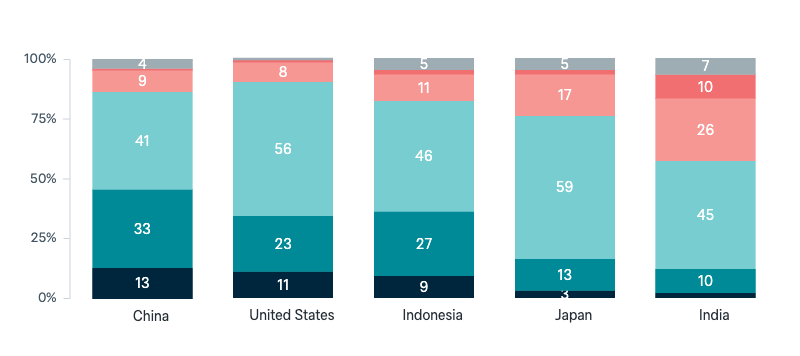
Australian foreign policy
Australia’s bilateral relationships under the Rudd government
Since the Rudd government was elected in November 2007, do you think Australia’s relations with each of the following countries are now better or worse?
Asked in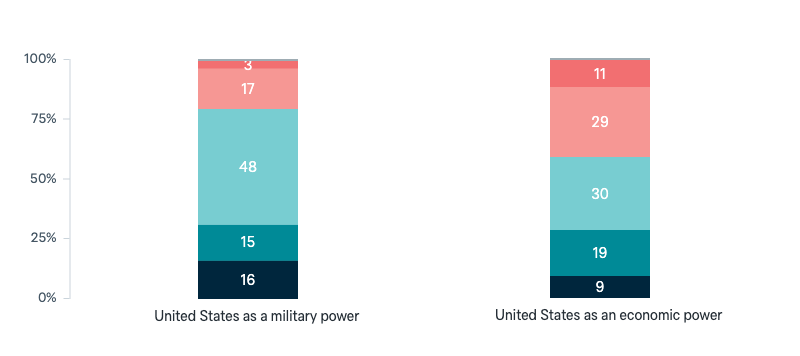
United States
US power in the coming decade
Do you think the United States will be stronger or weaker as an economic and military power in the next ten years?
Asked in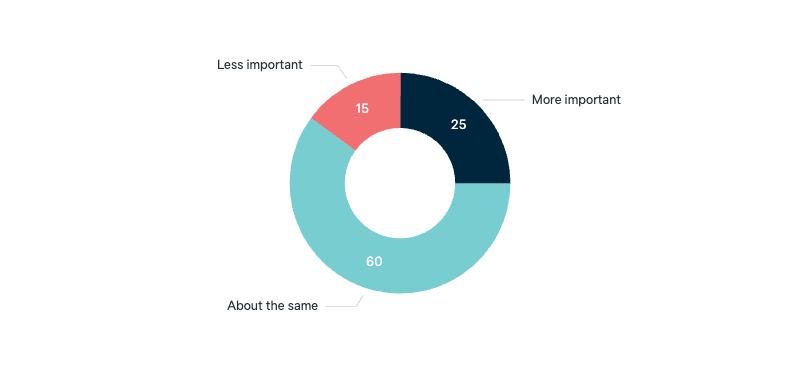
United States
Changing importance of ANZUS
Do you think our alliance with the United States is becoming more important, less important or is the importance of the alliance about the same?
Asked in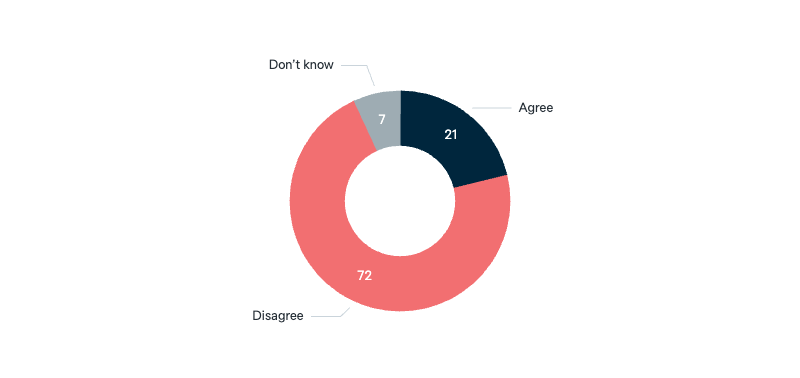
Relations in the Indo-Pacific
War over Taiwan
Should Australia act in accordance with ANZUS even if it means going to war with China over the independence of Taiwan?
Asked in